CLIENT
United Nations Environment Programme
PURPOSE
To communicate and celebrate 30 years of international effort in protecting the ozone layer.
DESCRIPTION
A campaign that includes a series of animations, visual images, print and online communication tools to help communicate what the ozone layer is, where it is in the atmosphere and what has been achieved under the ozone protection regime.
Thirty years ago the first images of the ozone hole created a media storm and helped lead to the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer and the Montreal Protocol.
People only had to look at a picture to physically see atmospheric chemistry. It didn’t take much persuasion to convince the policy makers to take action.
Pawan Bhartia, NASA atmospheric scientist
Carbon Visuals was honoured to be asked to create a digital campaign to communicate and celebrate the 30th anniversary of this event. We did not want to ‘re-invent the wheel’ so we started by researching what we felt was missing from ozone communications to date.
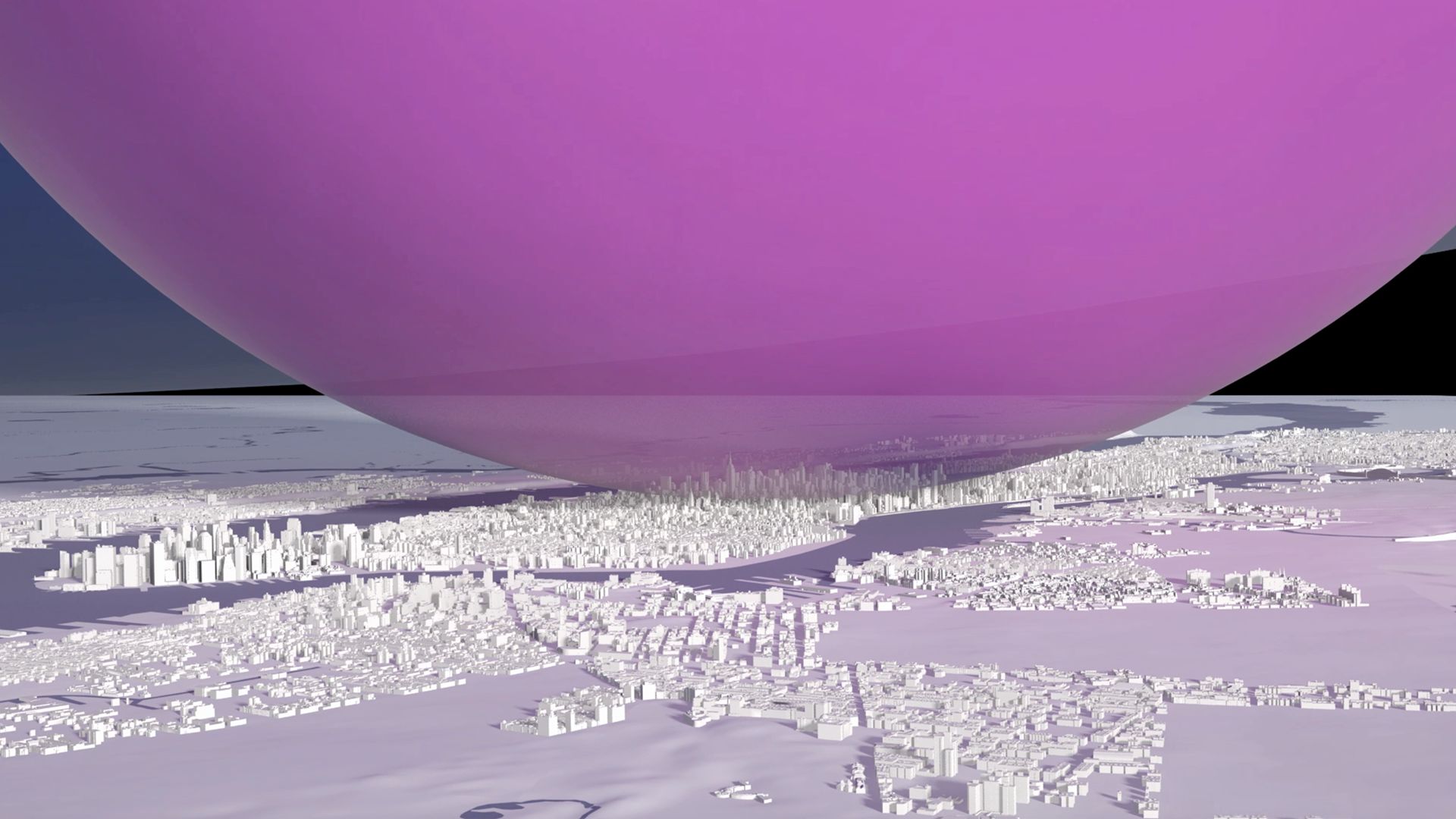
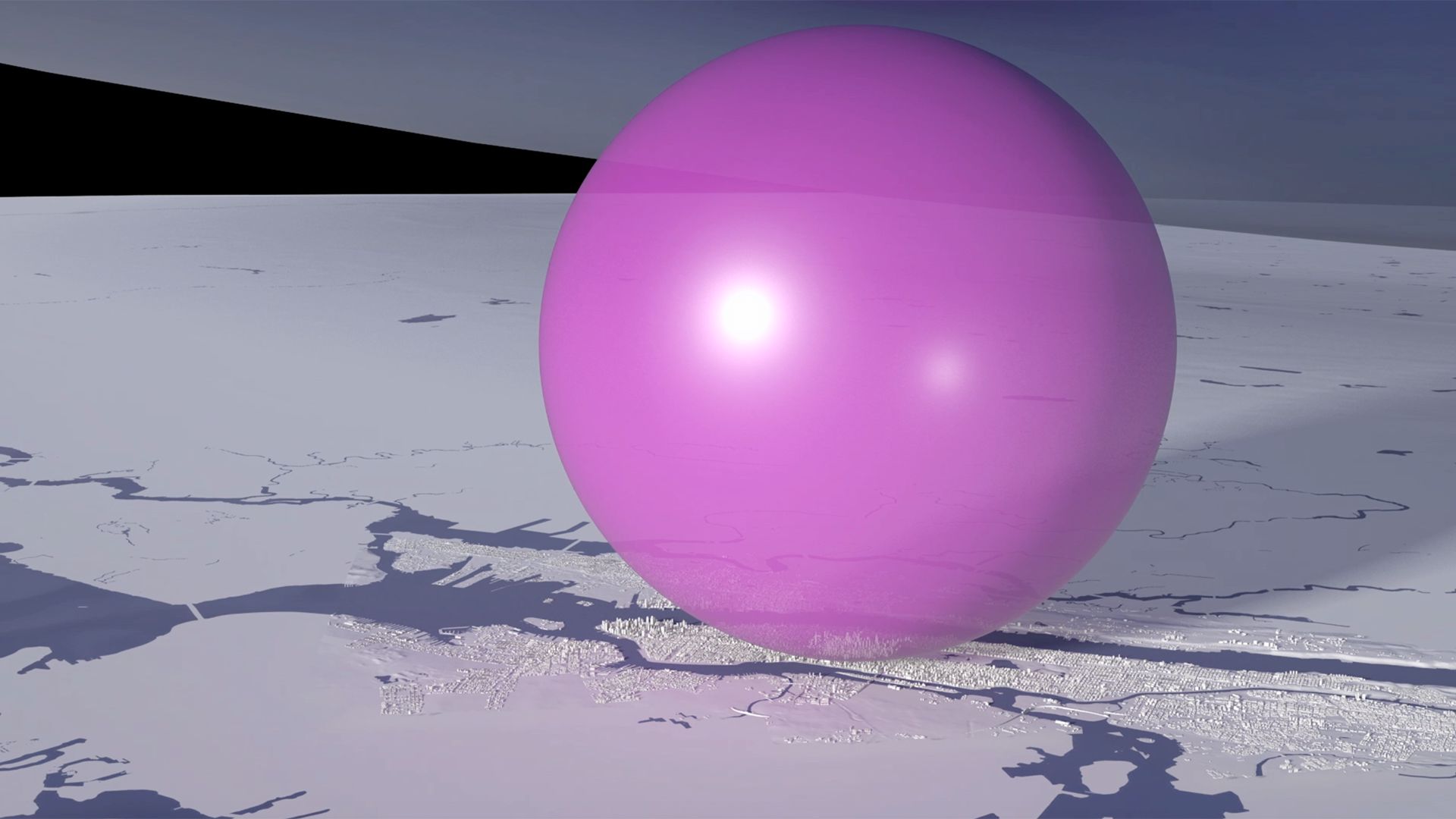
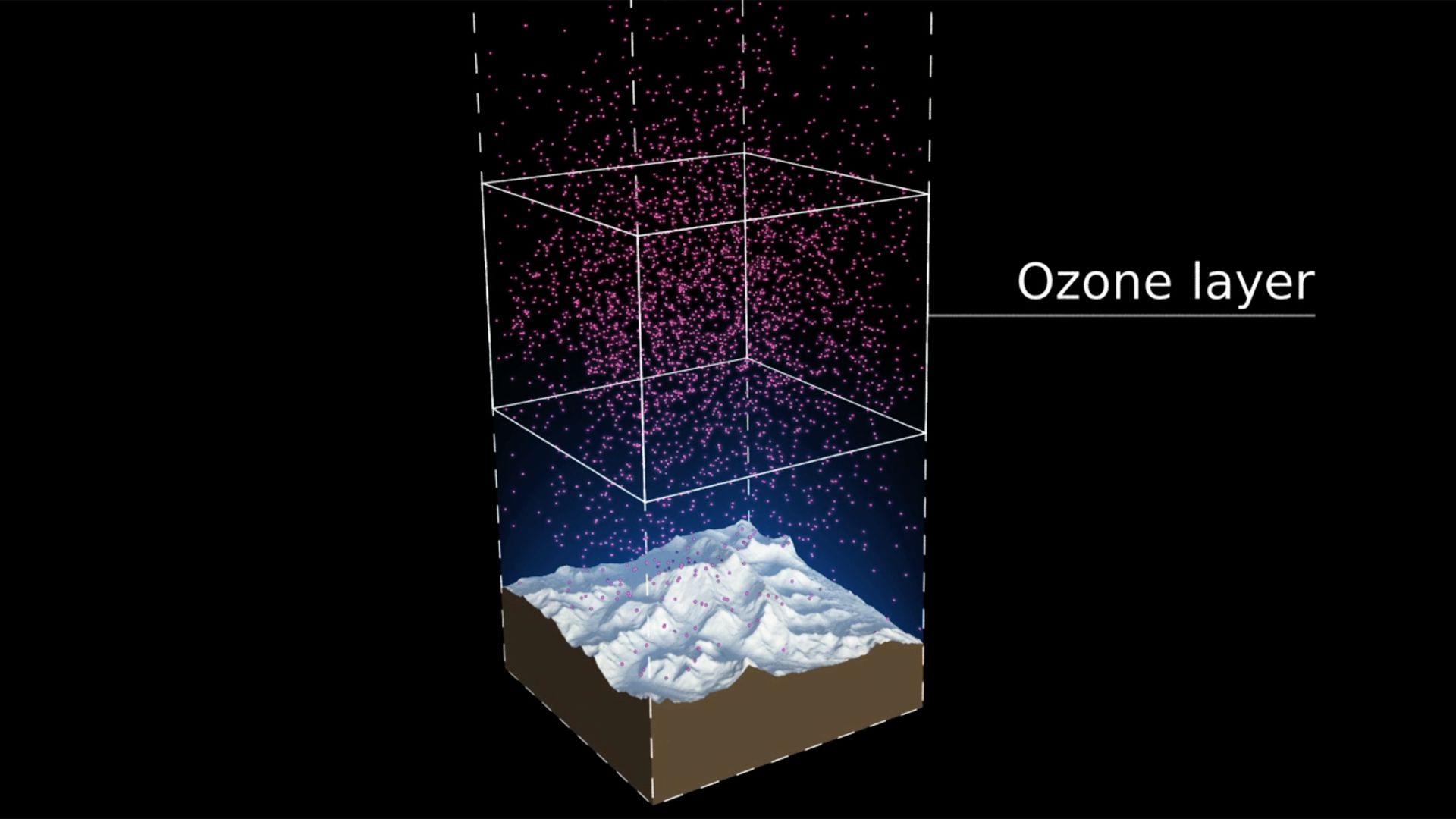
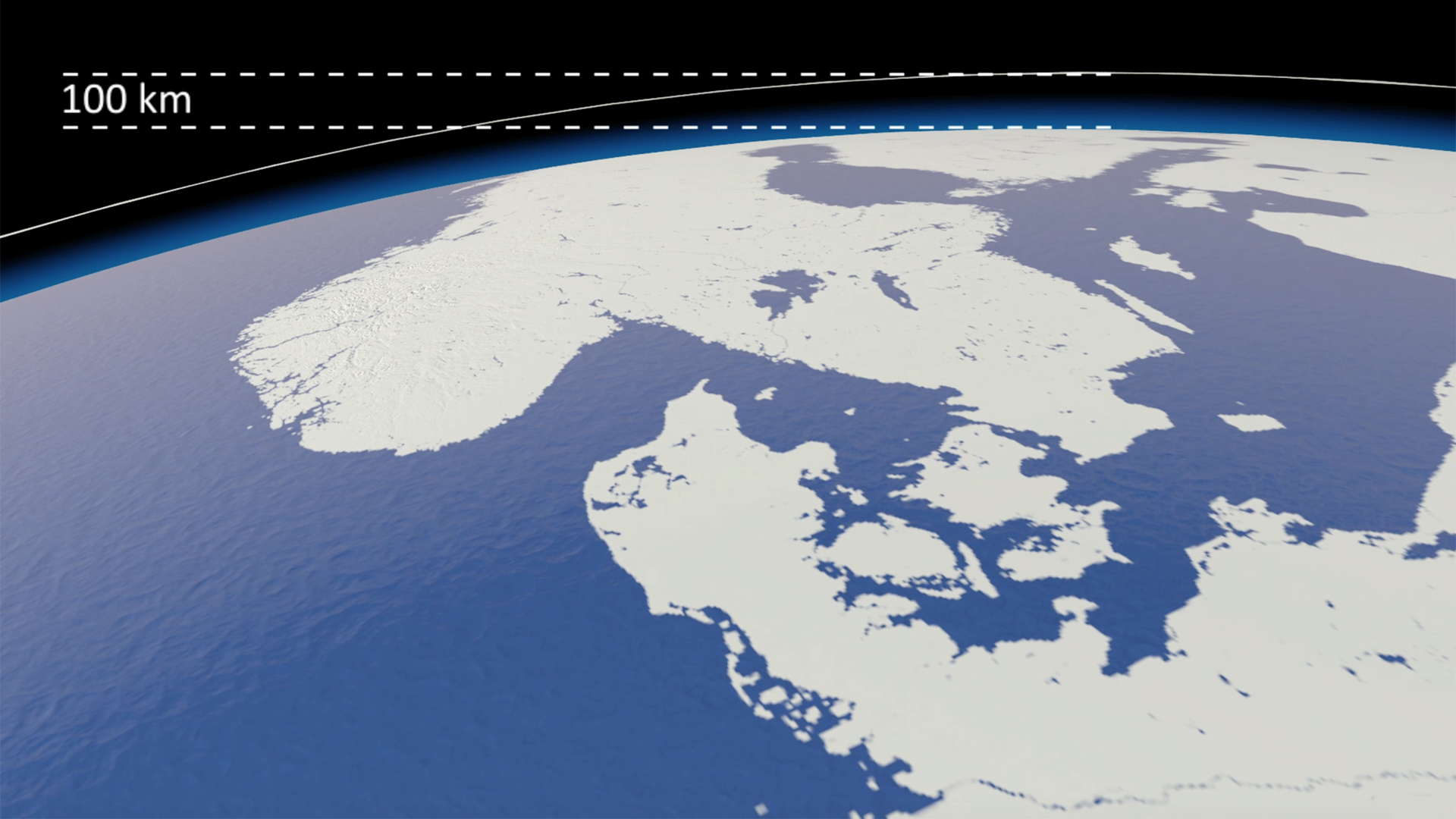
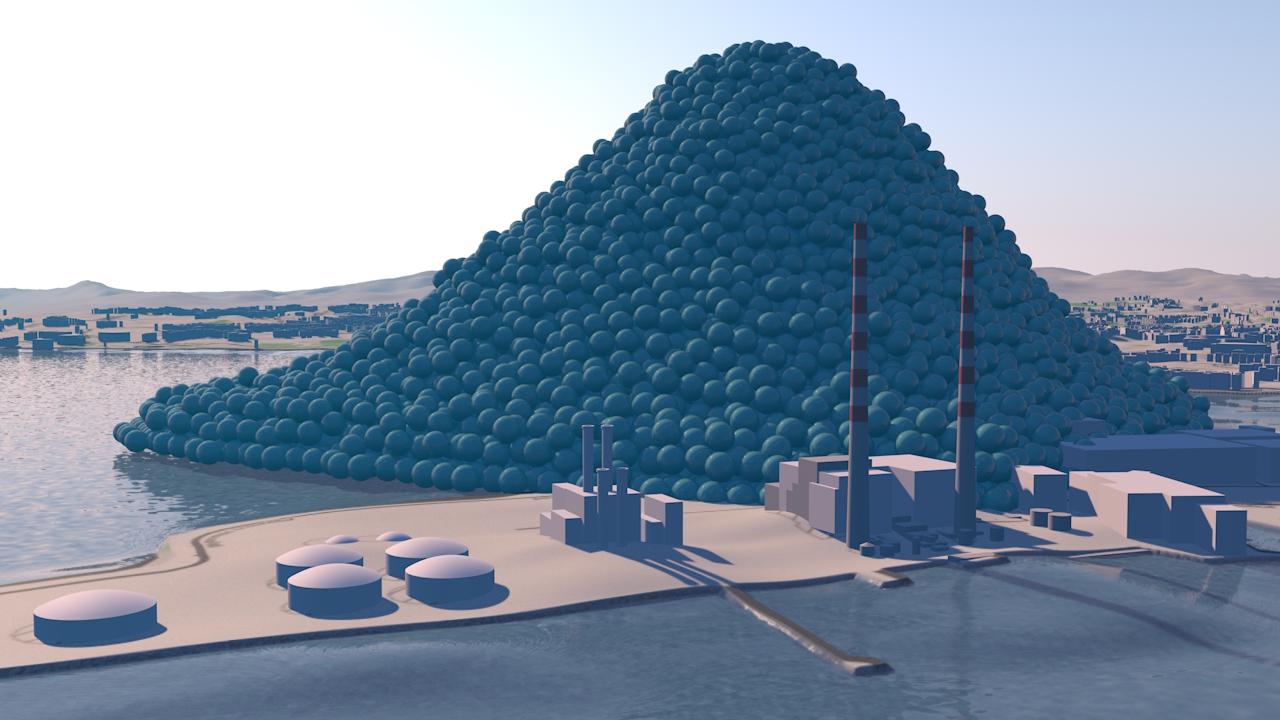
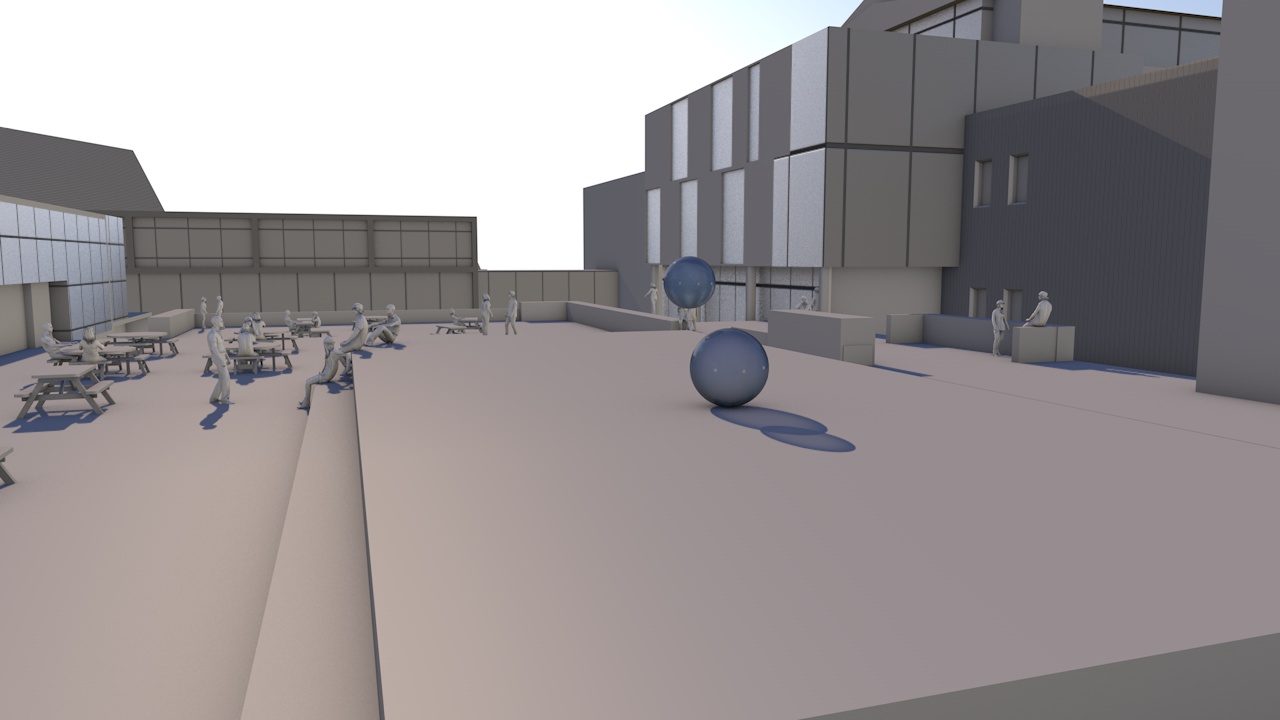
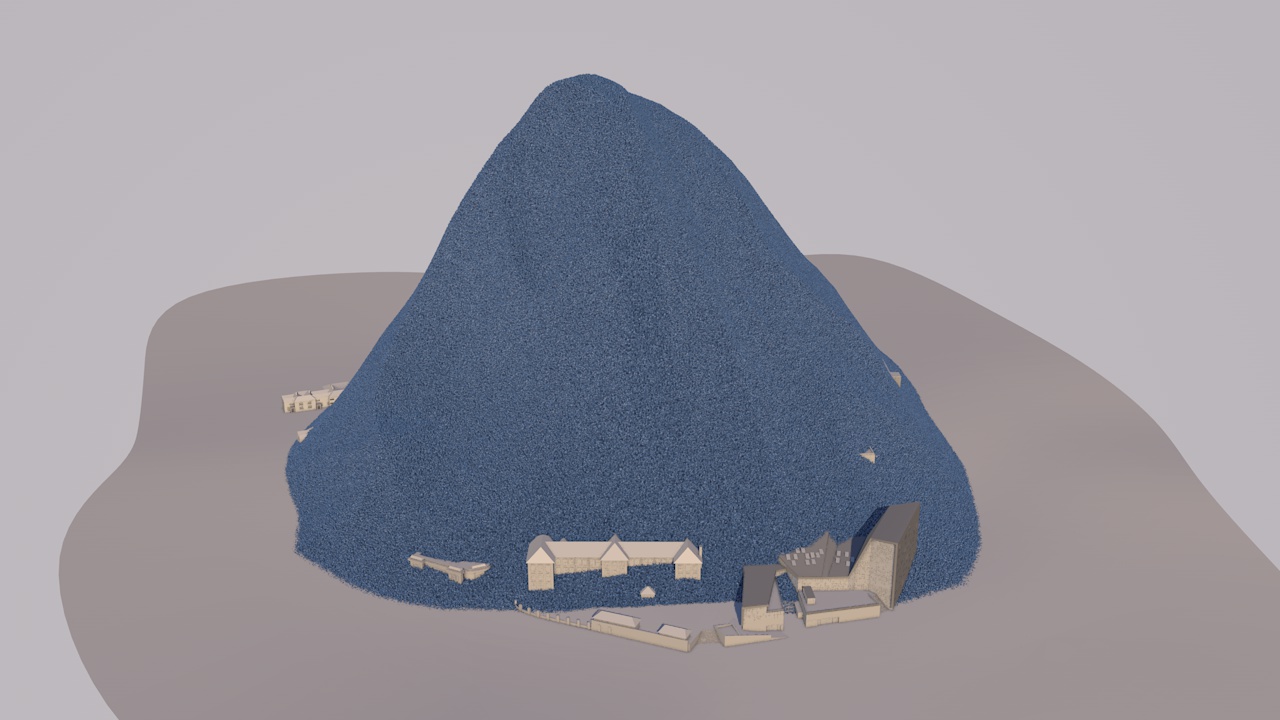
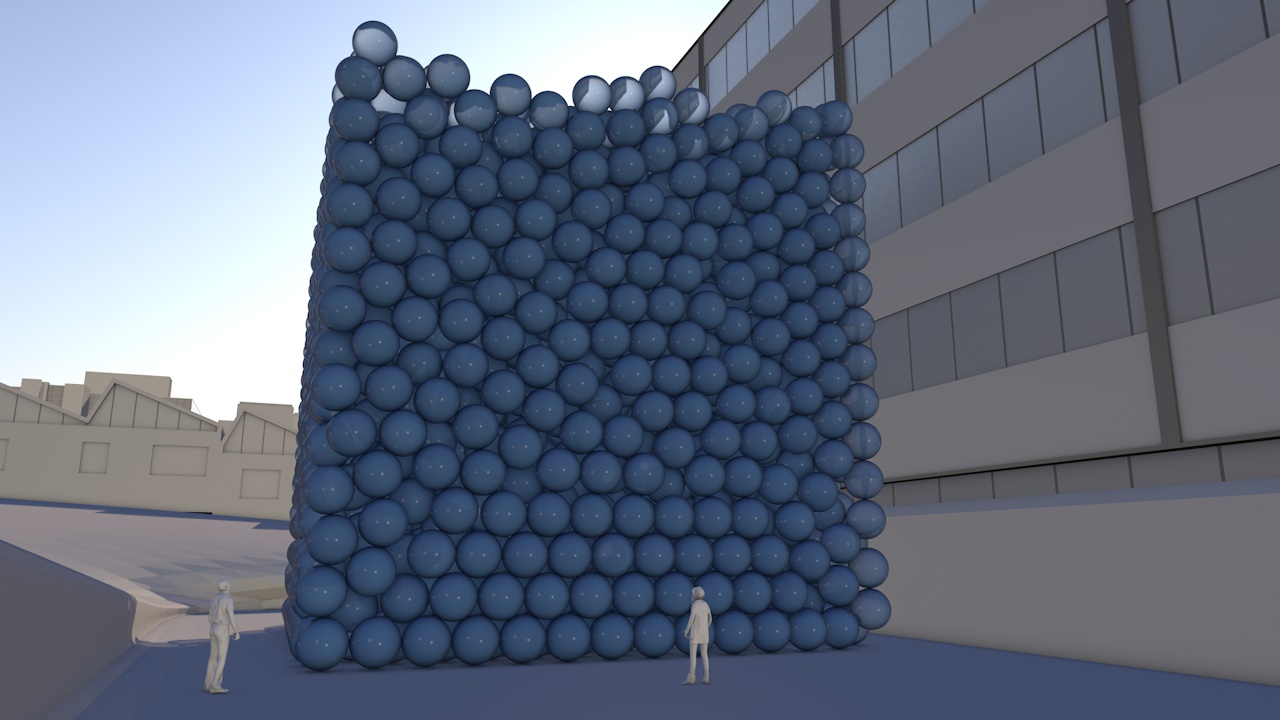
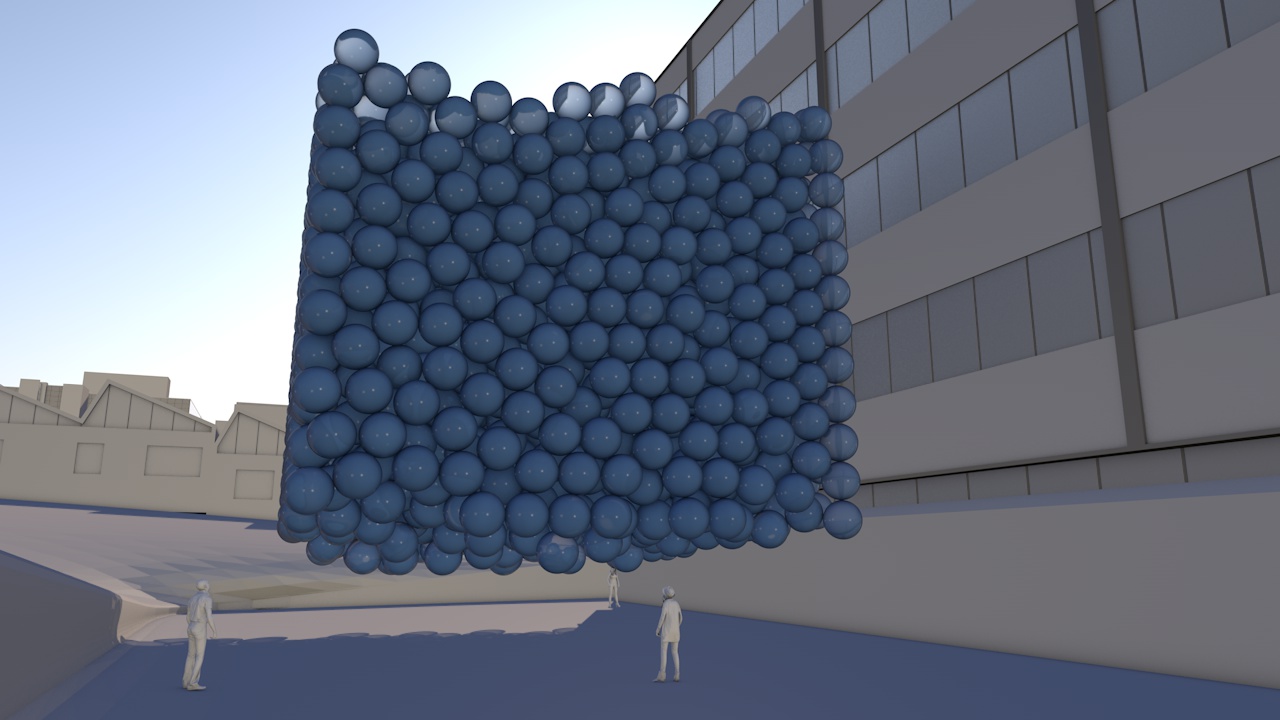
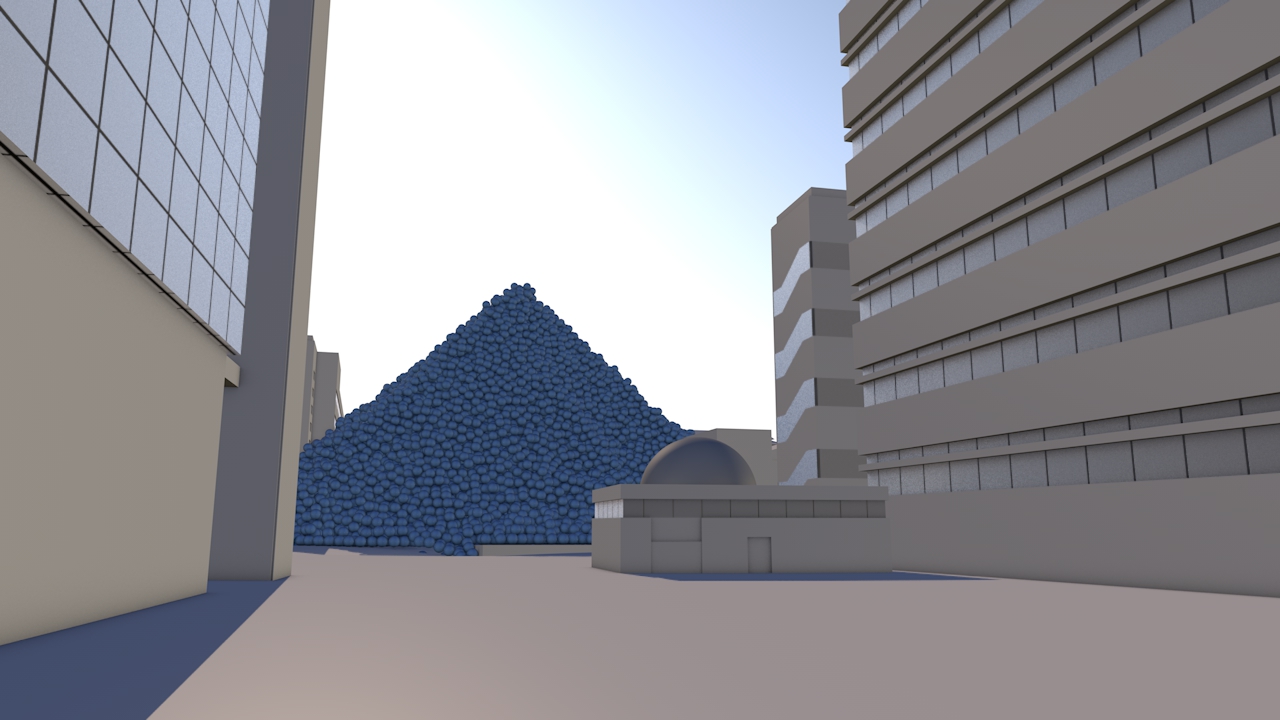
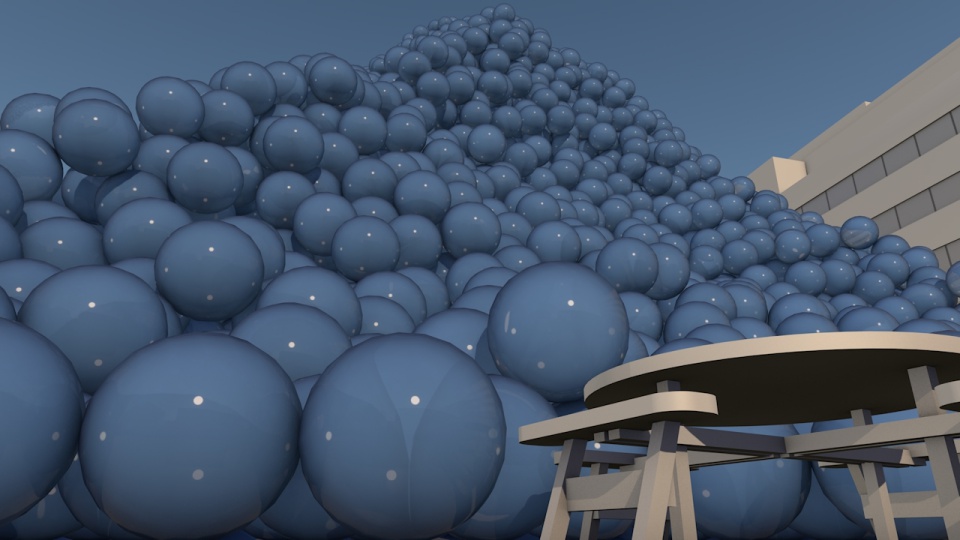
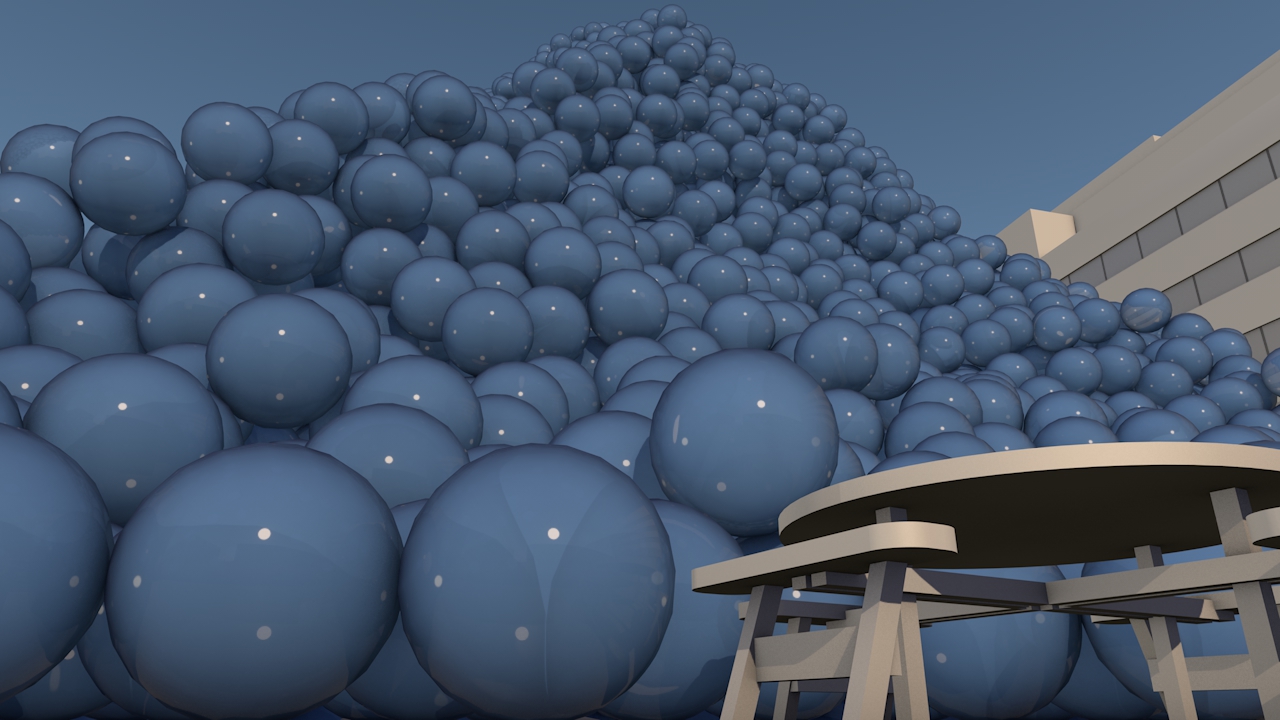
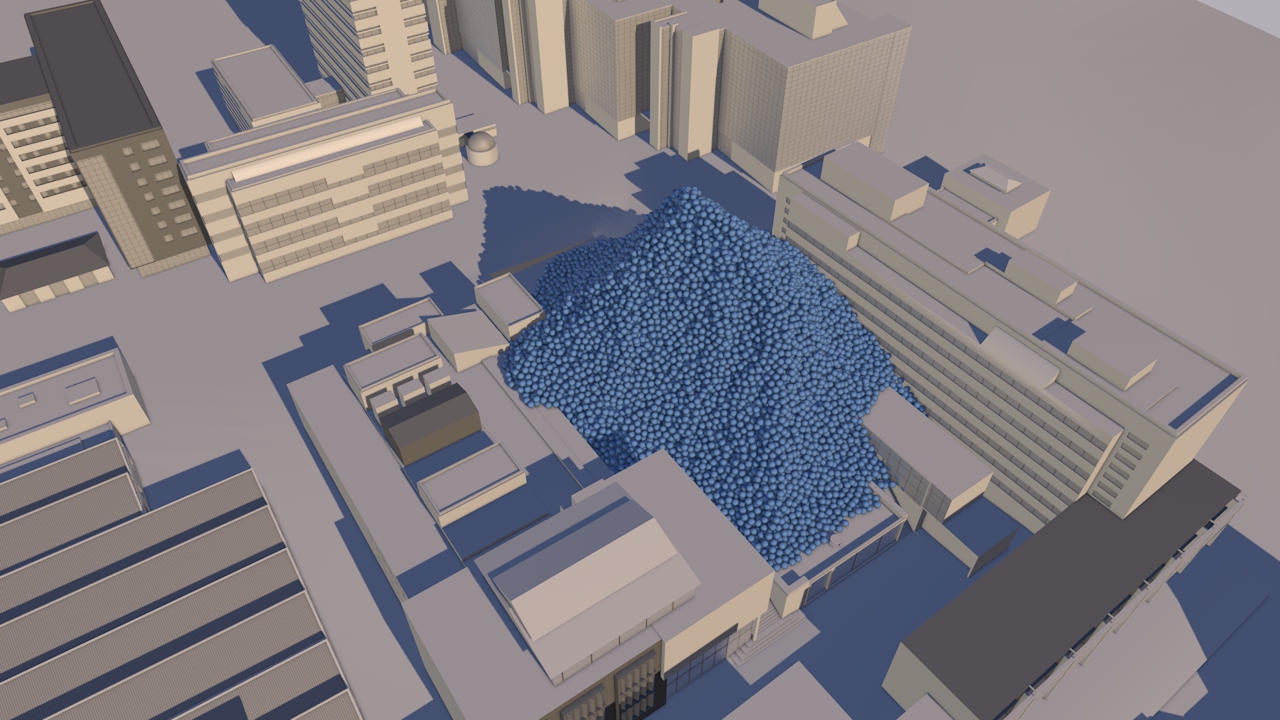
Our view was that few people have an intuitive sense of what the ozone hole is like, where it is, how much ozone there is, or how deep the atmosphere is. So we have created a selection of visual images, animations and web-tools that help everyone from policymakers to children better understand these things.
Over the coming months different elements will be releasedalongside key events within the UNEP calendar. This week, July 20-23, we are releasing two elements.
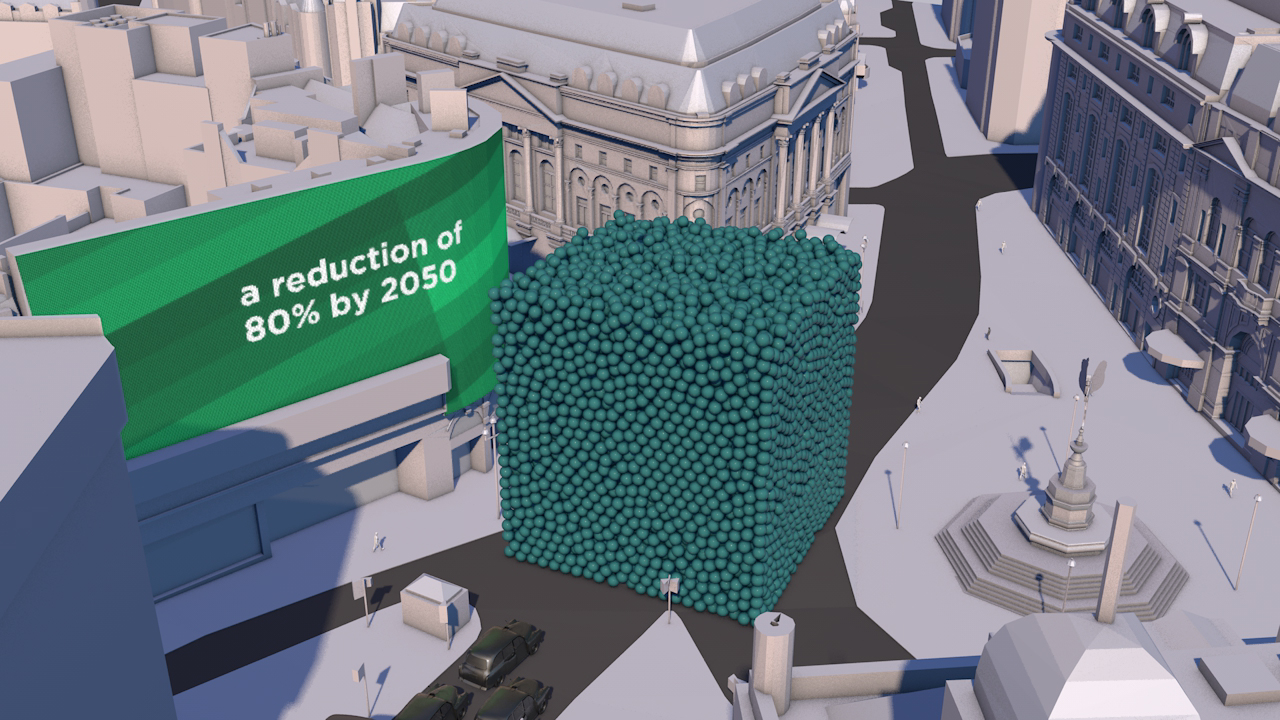
Precious ozone - the size of it
A short animation and a set of still images give viewers a sense of scale for how much air there is in the atmosphere and how much of it is ozone.
Click here to view on Youtube.
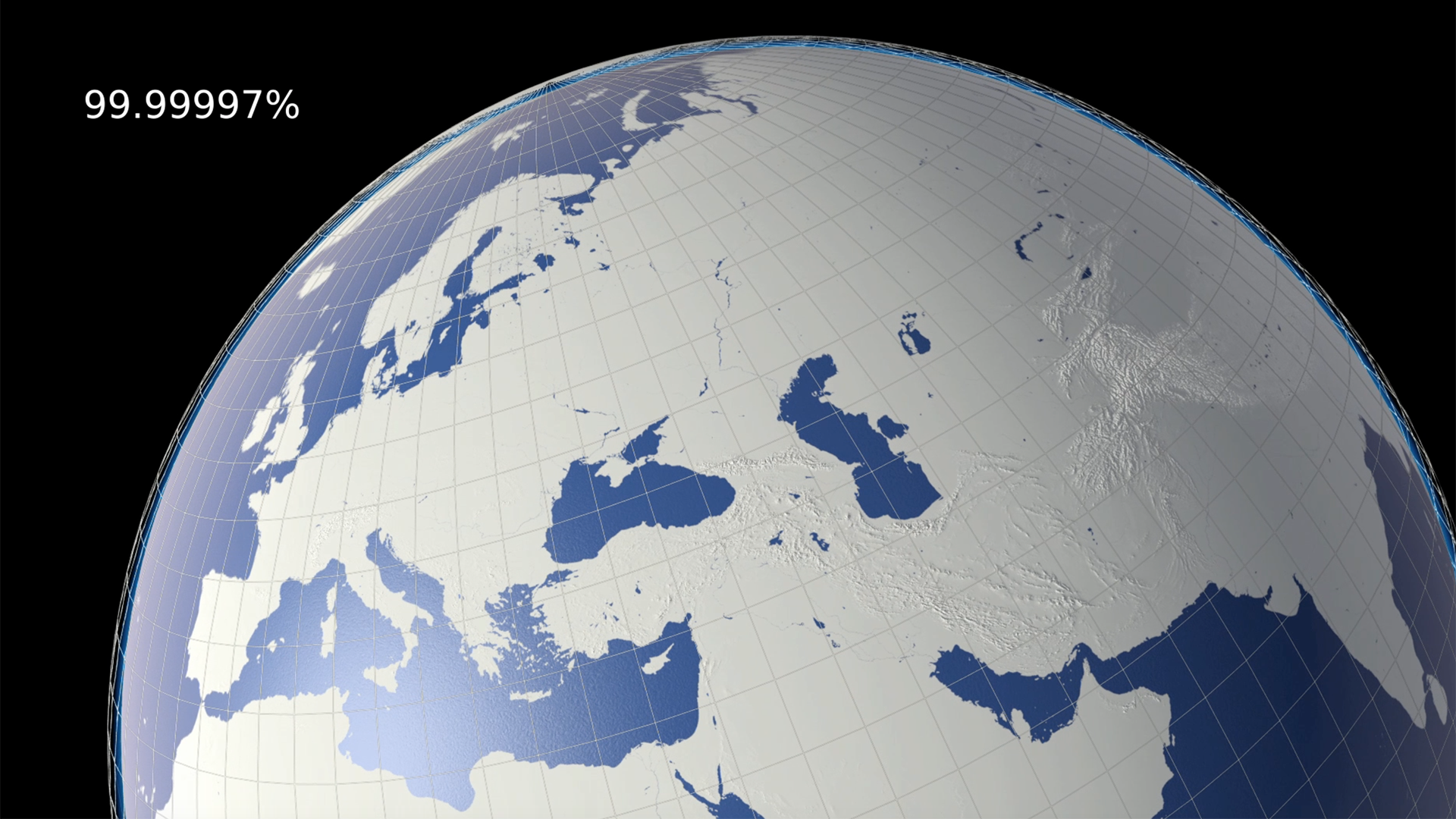
Ozone Globe
An interactive / self-running globe that displays current ozone distribution and also celebrates each country’s ratification of the Vienna Convention.
Click here to visit the interactive
All images are available under Creative Commons licence to download on our Flickr page
UN Ozone website: http://ozone.unep.org/en/infomaterials.php